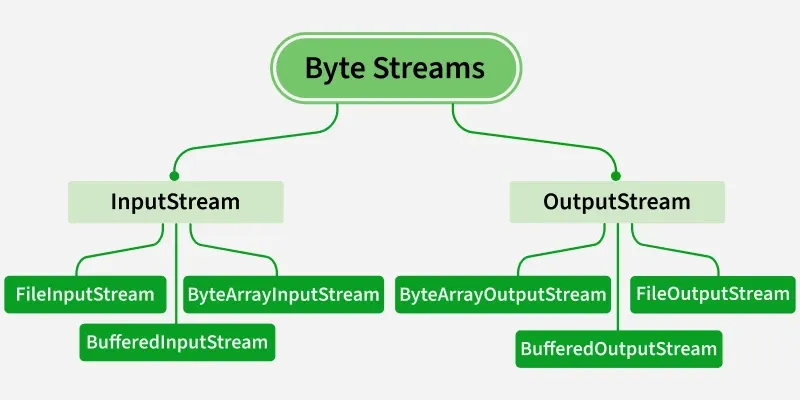
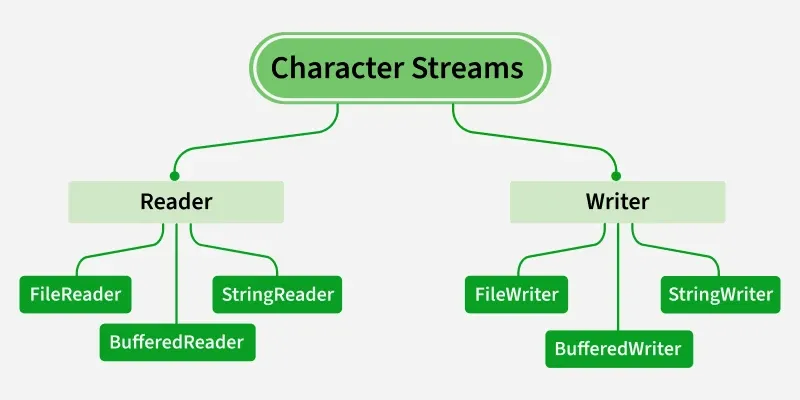
"I/O" means Input and Output. Java I/O is used to perform read and write operations with various sources like files, networks, keyboards, etc.
📥 Input
Reading data from keyboard, file, network, etc.
Example: Reading from a file
📤 Output
Writing data to file, screen, network, etc.
Example: Writing to a file
Java I/O is part of the java.io package and provides abstractions for reading and writing data.